Partitioning in SQL server with small sample:
Summary: Table partitioning can make very large tables and indexes easier to manage, and improve the performance of appropriately filtered queries.
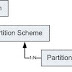
Table Partitioning Components:
The partition function, partition scheme, and partitioned table or index form a dependency tree, with the partition function at the top, the partition scheme depending on the partition function, and then the partitioned table or index depending on being linked to a partition scheme.

Partition function:
The partition function defines the boundary values of the initial set of partitions and the data type of the partitioned column:
o It makes no reference to any tables or disk storage.
o It forms the basis for one or more partition schemes.
create PARTITION function PF_dept(int)
AS range right FOR values (10,20,30)
Partition scheme:
The partition scheme maps particular partitions to filegroups:
o A given partition scheme can be used for one or more partitioned tables, indexes, and indexed views.
create partition scheme ps_dept
as partition PF_dept
TO (FG1,FG2,FG3,FG4)
Partitioned table:
The partitioned table or index is tied to a particular partition scheme when it is created:
o The partition table has only an indirect relationship, through the partition scheme, to the partition function.
create table dept
(deptid int,
deptname varchar(10)
)
ON ps_dept(deptid)
CREATE TABLE EMP
(EMPID INT,
EMPNAME VARCHAR(10),
DEPT_ID INT)
ON PS_DEPT(DEPT_ID)